Are you thinking about starting your Korean learning journey? Well, then you’ve come to the right place.
Korean is a beautiful language, spoken by over 80 million people from all around the world. Whether you like it cause of a Netflix show or a friend, you’re probably wondering:
Is Korean hard to learn?
From its unique script, Hangul, to distinct grammar structures, we’ll delve into the challenges and rewards that come with learning Korean.
Let’s not waste any time and get right into it.
Background of the Korean Language

Korean, or 한국어 (Hangugeo), has a rich history dating back 2,000 years on the Korean Peninsula. Its unique writing system, 한글 (Hangul), introduced in the 15th century, features 14 consonants and 10 vowels, providing a logical and accessible foundation.
The language follows a subject-object-verb (SOV) structure, adding a distinctive syntactical pattern. Politeness and formality are key in Korean communication, with honorifics and varied verb endings reflecting social nuances.
While Hangul is predominant, historical ties include Chinese characters, influencing Korean writing. This linguistic background enhances our appreciation of Korean’s beauty and complexity, laying a solid foundation for those exploring its challenges and rewards.
Why Is Korean Hard to Learn?
Learning any language comes with its set of challenges, and Korean is no exception. Understanding the difficulties can better prepare learners for the journey ahead.
Challenges to Consider when Learning Korean:
1. Script Complexity:
One aspect that makes Korean challenging is its unique script, Hangul. While designed for simplicity, mastering the 14 basic consonants and 10 vowels can be initially overwhelming. However, this script’s logic contributes to enhanced phonetic understanding once grasped.
2. Grammar Structure:
Korean features a subject-object-verb (SOV) sentence structure, differing from English’s subject-verb-object (SVO) arrangement. This shift can be perplexing for learners adjusting to a new grammatical order.
3. Politeness Levels:
The Korean language emphasizes politeness, with various levels of formality and honorifics. Navigating these social nuances adds a layer of complexity for learners unaccustomed to such linguistic intricacies.
4. Cultural Context:
Language is deeply entwined with culture, and Korean is no exception. Understanding cultural references, idioms, and historical contexts is essential for effective communication, posing an additional challenge for learners unfamiliar with Korean culture.
5. Limited Exposure:
Compared to widely spoken languages, Korean may have limited exposure in some regions. This can result in fewer immersion opportunities, making it challenging for learners to practice and reinforce their skills consistently.
Despite these challenges, it’s important to note that every language has its hurdles, and what may be difficult for one learner could be easier for another.
Approaching the process with patience, dedication, and an awareness of these challenges can significantly contribute to a more successful learning experience.
What Makes Korean Easy to Learn?
Korean can be considered easy to learn for many people, but it also depends on a few factors. For example, if your native language is Chinese, then it’s way easier to learn Korean than if your native language is English.
While Korean presents its challenges, there are several aspects that make it surprisingly easier for learners.
1. Logical Script:
The Hangul writing system, with its 14 basic consonants and 10 vowels, is not just visually intuitive but also logically designed. Once the script is understood, learners find it easier to read and pronounce words accurately.
2. Phonetic Pronunciation:
Korean pronunciation closely matches its written form. Unlike some languages where pronunciation can be tricky, Korean’s phonetic nature simplifies the process of learning how words sound based on their written representation.
3. No Grammatical Gender:
Unlike many European languages, Korean doesn’t have grammatical gender for nouns. This means learners don’t have to navigate the complexities of assigning gender to inanimate objects, streamlining the language learning process.
4. Verb Conjugation Simplicity:
While Korean verbs undergo conjugation, the process is generally straightforward compared to some other languages. Regular patterns make it easier for learners to grasp how verbs change based on tense and formality.
5. No Plural Forms:
Korean doesn’t use distinct plural forms for nouns. The same word is used for both singular and plural, simplifying the rules for learners. This is in contrast to languages where plural forms can be irregular and require memorization.
6. Consistent Sentence Structure:
Korean follows a consistent subject-object-verb (SOV) sentence structure. Once learners become accustomed to this pattern, constructing sentences becomes more predictable and manageable.
7. Language Learning Resources:
With the growing popularity of Korean culture globally, there is an abundance of resources available for learners. From language apps to online courses and cultural immersion experiences, these resources contribute to a supportive learning environment.
While every language has its intricacies, acknowledging the aspects that make Korean easy to learn can boost learners’ confidence and motivation. Approaching the language with an understanding of its friendly features can turn the journey into an enjoyable and rewarding experience.
How Long Does It Take to Learn Korean Fluently?
The timeframe to achieve fluency in Korean varies based on individual factors such as prior language learning experience, consistent practice, study methods, dedicated study time, and specific language goals.
Generally, individuals with prior language learning experience and consistent daily practice may achieve basic conversational skills within 6 months to a year, intermediate proficiency within 1 to 2 years, and advanced fluency within 2 to 3 years or more.
However, these are rough estimates, and the key to success lies in persistence, a well-structured study plan, and an immersive approach to language learning, with the understanding that individual experiences may vary.
Estimating Time Frames:
- Basic Conversational Skills: 6 months to a year.
- Intermediate Level: 1 to 2 years.
- Advanced Fluency: 2 to 3 years or more.
Is Korean Grammar and Alphabet Hard to Learn?
When delving into the realm of the Korean language, learners often encounter questions about the difficulty of its grammar and alphabet. Let’s break it down:
Hangul – The Korean Alphabet
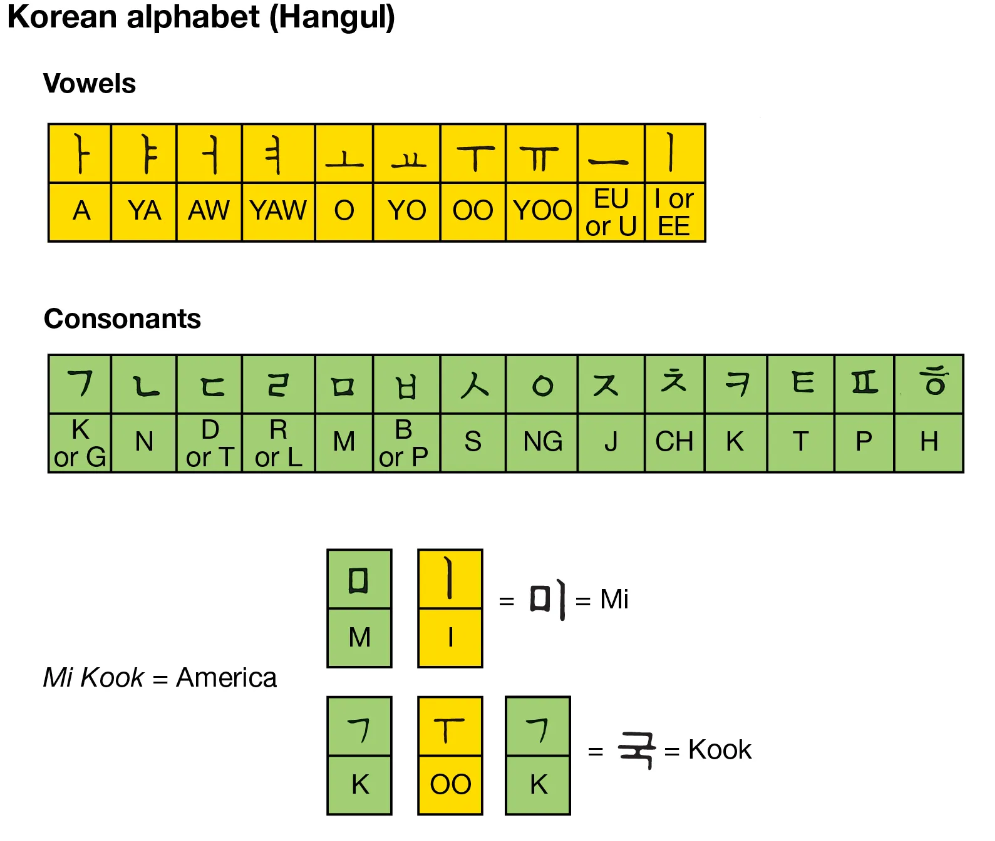
Learning Hangul, the Korean alphabet, is a distinctive aspect of starting your Korean journey. The good news is that Hangul is intentionally designed for simplicity. With 14 basic consonants and 10 vowels, it is both logical and visually intuitive. While it might seem unfamiliar at first, many learners appreciate its straightforward structure once they grasp the fundamentals.
Korean Grammar
Korean grammar differs from English, presenting a unique set of rules. The subject-object-verb (SOV) sentence structure may initially pose a challenge for English speakers accustomed to a subject-verb-object (SVO) order. However, the consistent application of grammar rules and logical patterns in Korean sentences contributes to a systematic and organized language structure.
So, while the initial encounter with Hangul and Korean grammar may seem daunting, they are designed to be learned efficiently. With the right resources, regular practice, and a positive mindset, mastering the Korean alphabet and grammar can become a rewarding and achievable endeavor.
Is Korean Hard to Learn for English Speakers?

Learning Korean can present challenges for English speakers due to differences in sentence structure, writing system, and linguistic nuances.
The subject-object-verb (SOV) structure and the unique Hangeul script may initially be unfamiliar.
Politeness levels and verb conjugations add complexity, but similarities, like the lack of grammatical gender and distinct plural forms, offer familiarity. Korean pronunciation aligns well with its written form, simplifying the learning process.
Accessible resources, including apps like Babbel, or Duolingo, and online courses from Skillshare or Udemy, make the journey more manageable.
While there are hurdles, English speakers with dedication and effective study methods can find learning Korean both rewarding and achievable.
Is It Worth It to Learn The Korean Language?
Deciding whether to learn the Korean language depends on various factors and individual goals.
Korean proficiency offers unique advantages, especially considering the global popularity of Korean entertainment, music, and cultural exports.
Learning Korean can provide access to a rich cultural tapestry, fostering a deeper understanding of Korean traditions, literature, and history. It opens doors to engaging with Korean media without reliance on translations.
Moreover, as South Korea continues to be a significant player in technology, business, and innovation, proficiency in Korean can enhance career opportunities and global communication.
Ultimately, the decision to learn Korean hinges on personal interests, cultural curiosity, career aspirations, and a willingness to embrace the rewards of linguistic and cultural enrichment.
If you try your best, you won’t regret learning Korean after all!
What Is The Best Way to Learn Korean?

When embarking on the journey to learn Korean, diverse resources cater to different preferences and learning styles.
1. Learning Korean Through Learning Apps:
Language learning apps such as Pimsleur, Babbel, and Rosetta Stone offer interactive lessons, gamified exercises, and progress tracking. These apps provide a convenient way to learn Korean on the go, making it suitable for those with busy schedules.
2. Learning Korean Through Online Courses:
Enrolling in online courses, whether through platforms like Skillshare, Udemy, or dedicated language learning websites, provides structured lessons and often includes video lectures, quizzes, and assignments. This approach suits learners who thrive on a more formal and comprehensive learning experience.
3. Learning Korean Through Podcasts:
Korean language podcasts, like Talk to Me in Korean and KoreanClass101, offer audio content covering various language aspects. Listening to native speakers enhances pronunciation and comprehension skills, making podcasts an excellent supplement to other learning methods.
4. Learning Korean Through Books:
Textbooks, workbooks, and comprehensive guides play a crucial role in learning Korean grammar, vocabulary, and cultural nuances. Popular choices include the “Integrated Korean” series and “Korean Grammar in Use.” Books provide an in-depth understanding and serve as valuable reference materials.
5. Learning Korean Through Conversational Platforms:
Engaging with conversational platforms like HelloTalk and Tandem connects learners with native Korean speakers for language exchanges. Practicing in real-life conversations helps reinforce what you’ve learned and provides cultural insights, enhancing both speaking and listening skills.
In crafting the best approach to learn Korean, a combination of these resources tailored to individual preferences, schedules, and goals often yields the most effective and enjoyable results.
My 7 Tips to Make Learning Korean Easy and Fun
Starting on the journey to learn Korean can be both enjoyable and rewarding. Here are five practical tips to make the process easy and fun:
1. Embrace Hangul Early:
Start by familiarizing yourself with the Hangul script from the beginning. Understanding the basics of Korean characters lays a solid foundation for reading and pronunciation.
2. Leverage Language Apps:
Incorporate language learning apps like Duolingo, Memrise, or Drops into your routine. These apps offer bite-sized lessons, interactive exercises, and game-like challenges, making learning Korean engaging and accessible.
3. Immerse Yourself in Korean Media:
Dive into Korean dramas, movies, music, and variety shows. Exposure to authentic language in various contexts enhances vocabulary, comprehension, and cultural understanding, making learning more enjoyable.
4. Practice Regularly with Language Partners:
Engage in language exchanges with native Korean speakers through platforms like HelloTalk or Tandem. Regular conversations enhance speaking and listening skills while providing insights into Korean culture.
5. Celebrate Milestones:
Acknowledge and celebrate your progress. Learning a new language is a gradual process, and recognizing your achievements, no matter how small, boosts motivation and keeps the learning experience positive.
By integrating these tips into your Korean language learning routine, you not only make the process easier and more enjoyable but also set yourself up for success in mastering this fascinating language.
Wrap Up: Is Korean Hard to Learn?
In wrapping up our exploration on the question ‘is Korean hard to learn?’, we’ve navigated through the complexities and unique aspects that make up the Korean language. While challenges exist, from the initial intricacies of the script to understanding cultural nuances, the journey is ultimately a fulfilling one.
Korean invites learners with its logical script, cultural richness, and the promise of discovering new dimensions in entertainment, communication, and personal development. Overcoming the challenges becomes more achievable and enjoyable with the right mindset, resources, and learning strategies.
See the difficulties as opportunities to grow and celebrate every achievement, big or small. Successfully learning Korean is about commitment, regular practice, and maintaining a genuine passion for the language and its culture.
As you step into the realm of learning Korean, remember that the journey is as important as reaching proficiency. So, is Korean hard to learn? Yes, to some extent, but with the right approach, it transforms into a rewarding and enriching adventure.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Is learning Hangul essential for mastering Korean?
Yes, understanding Hangul, the Korean script, is fundamental. It forms the basis for pronunciation and reading, making it an essential component of learning Korean.
2. How long does it typically take to become fluent in Korean?
The timeframe varies, but achieving basic conversational skills can take around 6 months to a year. Intermediate proficiency may take 1 to 2 years, while advanced fluency could take 2 to 3 years or more, depending on individual factors.
3. Are language apps sufficient for learning Korean, or should I combine multiple resources?
While language apps provide valuable lessons, combining resources such as online courses, books, and immersive experiences enhances the learning process. A diverse approach is often more effective.
4. Can I learn Korean without formal classes?
Absolutely. Many learners successfully acquire Korean through self-study using online resources, language apps, and immersion experiences. Formal classes are beneficial but not strictly necessary.
5. How can I practice speaking Korean if I don’t have native speakers around me?
Utilize language exchange platforms like HelloTalk or Tandem to connect with native Korean speakers for virtual language exchanges. It’s an effective way to practice speaking even if you’re not in a Korean-speaking environment.